Blockchain technology explained in simple words 用简单的话解释区块链技术
Blockchain technology is probably the best invention since the internet itself. It allows value exchange without the need for trust or a central authority. Imagine you and I bet $50 on tomorrow’s weather in San Francisco. I bet it will be sunny,you that it will rain. Today we have three options to manage this transaction: 區塊鏈技術可能是自互聯網以來最好的發明。它允許價值交換而無需信任或中央權威。假設您和我為明天的舊金山天氣下注$50。我敢打賭,天氣晴朗,你會下雨。今天,我們有三種選擇來管理此交易: We cantrusteach other. Rainy or sunny, the loser will give $50 to the winner. If we are friends, this could be a good way of managing it. However,friends or strangers, one can easily not pay the other. 我們可以互相信任。多雨或晴天時,失敗者將給獲勝者$ 50。如果我們是朋友,這可能是管理它的好方法。但是,無論是朋友還是陌生人,一個人都無法輕易付款。 We can turn the bet into acontract. With a contract in place both parties will bemore prone to pay. However, should either of the two decide not to pay, the winner will have to pay additional money to cover legal expenses and the court case might take a long time. Especially for a small amount of cash, this doesn’t seem like the optimal way to manage the transaction. 我們可以把賭注變成合同。有了合同,雙方將更傾向於付款。但是,如果兩者中的任何一個決定不支付,獲勝者將不得不支付額外的錢來支付法律費用,並且法庭案件可能需要很長時間。特別是對於少量現金,這似乎不是管理交易的最佳方法。 We can involve aneutral third party. Each of us gives $50 to a third party, who will give the total amount to the winner. But hey, she could also run away withall our money. Therefore, we end up with one of the first two options:trustorcontract. 我們可以讓中立的第三方參與其中。我們每個人都將$ 50贈予第三方,第三方將把總金額提供給獲勝者。但是,她也可以用我們所有的錢逃走。因此,我們最終得到了前兩個選擇之一:信任或契約。 Neither trust nor contract is an optimal solution: We can’t trust strangers, and enforcing a contract requires time and money. The blockchain technology is interesting because it offers us a third option which is secure, quick, and cheap. 信任和合同都不是最佳解決方案:我們不能信任陌生人,執行合同需要時間和金錢。區塊鏈技術很有趣,因為它為我們提供了安全,快速和廉價的第三種選擇。 Blockchain allows us to write a few lines of code, a program running on the blockchain, to which both of us send $50. This program will keep the $100 safe and check tomorrow’s weather automatically on several data sources. Sunny or rainy, it will automatically transfer the whole amount to the winner. Each party can check the contract logic, and once it’s running on the blockchain it can’t be changed or stopped. This may be too much effort for a $50 bet but imagine selling a house or a company. 區塊鏈允許我們編寫幾行代碼,這是一個在區塊鏈上運行的程序,我們倆都向該行發送了$50。該程序將確保$ 100的安全,並通過多個數據源自動檢查明天的天氣。晴天或雨天,它將自動將全部金額轉移給獲勝者。各方都可以檢查合同邏輯,一旦它在區塊鏈上運行,就無法更改或停止。對於50美元的賭注來說,這可能太費力了,但是想像一下如果是賣房子或公司。 This article explains how the blockchain works without discussing the technical details in depth, but by digging just enough to give you a general idea of the underlying logic and mechanisms. 本文在不深入討論技術細節的情況下解釋了區塊鏈的工作原理,而是通過深入挖掘以使您對底層邏輯和機制有一個總體瞭解。 Also available inSimplified ChineseandMandarinthanks to volunteering efforts and blockchain community support. 由於志願者的努力和區塊鏈社區的支持,還提供簡體中文和普通話版本。 The Basics of Bitcoin 比特幣的基礎
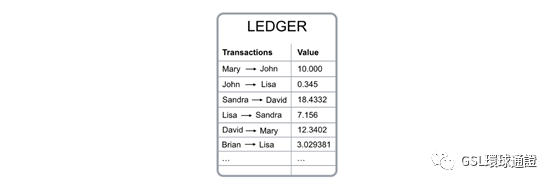
The most known and discussed application of the blockchain technology isbitcoin,a digital currency that can be used to exchange products and services, just like the U.S. dollar, euro, Chinese yuan, and other national currencies. Let’s use this first application of the blockchain technology to learn how it works. 區塊鏈技術最著名和討論最多的應用是比特幣,一種可以用來交換產品和服務的數字貨幣,就像美元,歐元,人民幣和其他本國貨幣一樣。讓我們使用區塊鏈技術的第一個應用程序來瞭解其工作原理。 “Bitcoin gives us, for the first time, a way for one Internet user to transfer a unique pieceof digital property to another Internet user, such that the transfer is guaranteed to be safe and secure, everyone knows that the transfer has taken place, and nobody can challenge the legitimacy of the transfer. The consequences of this breakthrough are hard to overstate.”—— MarcAndreessen “比特幣首次為我們提供了一種方式,一個互聯網用戶將獨特的數字資產轉讓給另一位互聯網用戶,從而確保了轉移的安全性,每個人都知道轉移已經發生,沒有人可以挑戰轉讓的合法性。這一突破的後果很難誇大。”——馬克·安德森(Marc Andreessen) One bitcoin is a single unit of the Bitcoin (BTC) digital currency. Just like a dollar, a bitcoin has no value by itself; it has value only because we agree to trade goods and services to bring more of the currency under our control, and we believe others will do the same. 一個比特幣是比特幣(BTC)數字貨幣的一個單位。就像美元一樣,比特幣本身沒有價值。它之所以具有價值,僅僅是因為我們同意貿易商品和服務,以使更多的貨幣受到我們的控制,而且我們相信其他人也會這樣做。 To keep track of the amount of bitcoin each of us owns, the blockchain uses aledger,a digital file that tracks all bitcoin transactions. 為了跟蹤我們每個人擁有的比特幣數量,區塊鏈使用分類帳(一個跟蹤所有比特幣交易的數字文件)。
Fig. 1 -Bitcoin ledger digital file simplified 圖1-簡化的比特幣分類帳數字文件 The ledger file is not stored in a central entity server, like a bank, or in a single data center. It is distributed across the world via a network of private computers that are both storing data and executing computations. Each of these computers represents a “node”of the blockchain network and has a copy of the ledger file. 分類帳文件並未存儲在中央實體服務器(如銀行)中或單個數據中心中。它通過存儲數據和執行計算的私有計算機網絡分佈在世界各地。這些計算機中的每一個都代表區塊鏈網絡的“節點”,並具有分類帳文件的副本。 If David wants to send bitcoins to Sandra, he broadcasts a message to the network that says the amount of bitcoin in his account should go down by 5 BTC, and the amountin Sandra’s account should increase by the same quantity. Each node in the network will receive the message and apply the requested transaction to its copyof the ledger, updating the account balances. 如果David想要將比特幣發送給Sandra,他向網絡廣播一條消息,說他帳戶中的比特幣數量應減少5 BTC,Sandra帳戶中的比特幣數量應增加相同數量。網絡中的每個節點都將接收到該消息,並將請求的交易應用於其賬本副本,從而更新帳戶餘額。
Fig. 2 -Transaction request message simplified 圖2-簡化交易請求消息 The fact that the ledger is maintained by a group of connected computers rather than bya centralized entity like a bank has several implications: In our bank system we only know our own transactions and account balances; on the blockchain everyone can see everyone else’s transactions. While you can generally trust your bank, the bitcoin network is distributed and if something goes wrong there is no help desk to call or anyone to sue. The blockchain system is designed in such a way that no trust is needed; security and reliability are obtained via special mathematical functions and code. 分類帳由一組連接的計算機而不是由銀行之類的集中式實體維護,這一事實有幾個含義: 在我們的銀行系統中,我們只知道自己的交易和帳戶餘額; 在區塊鏈上,每個人都可以看到其他人的交易。儘管您通常可以信任您的銀行,但比特幣網絡是分布式的,如果出現問題,則無需致電服務台或任何人起訴。 區塊鏈系統的設計無需信任。通過特殊的數學函數和代碼可獲得安全性和可靠性。 We can define the blockchain as a system that allows a group of connected computers to maintain a single updated and secure ledger. In order to perform transactionson the blockchain, you need awallet,a program that allows you to store and exchange your bitcoins. Since only you should be able to spend your bitcoins, each wallet is protected by a special cryptographic method that uses a unique pair of distinct but connected keys: aprivate and a public key. 我們可以將區塊鏈定義為一個系統,該系統允許一組連接的計算機維護單個更新且安全的分類帳。為了在區塊鏈上執行交易,您需要一個錢包,一個允許您存儲和交換比特幣的程式。由於只有您才能夠使用您的比特幣,因此每個錢包都受到一種特殊的加密方法的保護,該方法使用一對獨特但相互連接的密鑰對:私鑰和公鑰。 If a message is encrypted with a specific public key, only the owner of the paired private key can decrypt and read the message. The reverse is also true: If you encrypt a message with your private key, only the paired public key can decryptit. When David wants to send bitcoins, he needs to broadcast a message encrypted with the private key of his wallet. As David is the only one who knows the private key necessary to unlock his wallet, he is the only one who can spend his bitcoins. Each node in the network can cross-check that thetransaction request is coming from David by decrypting the message with thepublic key of his wallet. 如果消息是使用特定的公共密鑰加密的,則只有配對的私有密鑰的所有者才能解密和讀取該消息。反之亦然:如果您使用私鑰加密消息,則只有成對的公鑰才能解密該消息。當大衛想發送比特幣時,他需要廣播一條用他錢包的私鑰加密的消息。由於David是唯一知道解鎖錢包所需私鑰的人,因此他是唯一可以使用他的比特幣的人。網絡中的每個節點都可以使用其錢包的公鑰解密消息,從而交叉檢查交易請求是否來自David。 When you encrypt a transaction request with your wallet’s private key, you are generating a digital signature that is used by blockchain computers to verifythe source and authenticity of the transaction. The digital signature is astring of text resulting from your transaction request and your private key; therefore,it cannot be used for other transactions. If you change a single character inthe transaction request message, the digital signature will change, so no potential attacker can change your transaction requests or alter the amount of bitcoin you are sending. 當您用錢包的私鑰加密交易請求時,您將生成一個數字簽名,區塊鏈計算機將使用該數字簽名來驗證交易的來源和真實性。數字簽名是一串由您的交易請求和您的私鑰產生的文本;因此它不能用於其他交易。如果您更改交易請求消息中的單個字符,則數字簽名將更改,因此任何潛在的攻擊者都無法更改您的交易請求或更改您發送的比特幣數量。
Fig. 3 -Digital Signature transaction encryption simplified 圖3-簡化了數字簽名交易加密 To send bitcoin you need to prove that you own the private key of a specific wallet asyou need the key to encrypt your transaction request message. Since you broadcast the message only after it has been encrypted, you never have toreveal your private key. 要發送比特幣,您需要證明自己擁有特定錢包的私鑰,因為您需要該密鑰來加密交易請求消息。由於僅在消息加密後才廣播消息,因此您無需透露私鑰。 Tracking Your Wallet Balance 跟蹤您的錢包餘額 Each nodein the blockchain is keeping a copy of the ledger.So, how does a node know your account balance? The blockchain system doesn’t keep track of account balances at all; it only records every transaction that is verified and approved. The ledger in fact does not keep track of balances, it only keeps track of every transaction broadcasted within the bitcoin network (Fig. 4). To determine your wallet balance, you need to analyze and verify all the transactions that ever took place on the whole network connected to your wallet. 區塊鏈中的每個節點都保留著分類帳的副本。那麼,節點如何知道您的帳戶餘額?區塊鏈系統根本不跟蹤帳戶餘額;它僅記錄每筆經過驗證和批准的交易。實際上,分類帳不跟蹤餘額,僅跟蹤比特幣網絡中廣播的每個交易(圖4)。為了確定您的錢包餘額,您需要分析並驗證連接到您的錢包的整個網絡上發生的所有交易。
Fig. 4 -Blockchain Ledger 圖4-區塊鏈分類帳 This “balance”verification is performed based on links to previous transactions. In order tosend 10 bitcoins to John, Mary must generate a transaction request that includes links to previous incoming transactions that add up to at least 10 bitcoins. These links are called “inputs.” Nodes in the network verify the amount and ensure that these inputs haven’t been spent yet. In fact, each time you reference inputs in a transaction, they are deemed invalid for any future transaction. This is all performed automatically in Mary’s wallet and double-checked by the bitcoin network nodes; she only sends a 10 BTC transaction to John’s wallet using his public key. 該“餘額”驗證是基於到先前交易的鏈接執行的。為了將10個比特幣發送給John,Mary必須生成一個交易請求,該交易請求包括指向之前傳入交易的鏈接,這些鏈接加起來至少有10個比特幣。這些鏈接稱為“輸入”。網絡中的節點會驗證金額,並確保尚未花費這些輸入。實際上,每次您引用交易中的輸入時,它們對於以後的任何交易都被視為無效。所有這些操作都是在Mary的錢包中自動執行的,並由比特幣網絡節點仔細檢查;她僅使用他的公鑰向John的錢包發送了10 BTC交易。
Fig. 5 -Blockchain transaction request structure 圖5-區塊鏈交易請求結構 So, how can the system trust that input transactions are valid? It checks all the previous transactions correlated to the wallet you use to send bitcoins via the input references. To speed up the verification process, a special record of unspent transactions is kept by the network nodes. Thanks to this security check, it is not possible to double-spend bitcoins. 那麼,系統如何才能相信輸入交易有效?它檢查與您用於通過輸入引用發送比特幣的錢包相關的所有先前交易。為了加快驗證過程,網絡節點保留了未用交易的特殊記錄。由於進行了此安全檢查,因此無法雙重使用比特幣。 Owning bitcoins means that there are transactions written in the ledger that point toyour wallet address and haven’t been used as inputs yet. All the code toperform transactions on the bitcoin network is open source; this means that anyone with a laptop and an internet connection can operate transactions.However, should there be a mistake in the code used to broadcast a transaction request message, the associated bitcoins will be permanently lost. 擁有比特幣意味著賬本中有一些指向您的錢包地址的交易,尚未被用作輸入。在比特幣網絡上執行交易的所有代碼都是開源的。這意味著任何擁有筆記本電腦和互聯網連接的人都可以進行交易。但是,如果用於廣播交易請求消息的代碼有誤,則相關的比特幣將永久丟失。 Remember that since the network is distributed, there is no customer support to call nor anyone who could help you restore a lost transaction or forgotten wallet password. For this reason, if you are interested in transacting on the bitcoin network, it’s a good idea to use the open source and official version of bitcoin wallet software (such asBitcoin Core),and to store your wallet’s password or private key in a very safe repository. 請記住,由於網絡是分布式的,因此沒有客戶支持電話,也沒有任何人可以幫助您恢復丟失的交易或忘記的錢包密碼。因此,如果您有興趣在比特幣網絡上進行交易,最好使用開源和正式版本的比特幣錢包軟件(例如BitcoinCore),並將錢包的密碼或私鑰存儲在安全的存儲庫。 But Is It Really Safe? And Why Is It Called Blockchain? 但這真的安全嗎?為什麼稱之為區塊鏈? Anyone can access the bitcoin network via an anonymous connection (for example, theTOR networkor aVPN network),and submit or receive transactions revealing nothing more than his public key. However,if someone uses the same public key over and over, it’s possible to connect allthe transactions to the same owner. The bitcoin network allows you to generate as many wallets as you like, each with its own private and public keys. This allows you to receive payments on different wallets, and there is no way for anyone to know that you own all these wallets’ private keys, unless you send all the received bitcoins to a single wallet.The total number of possible bitcoin addresses is 2??? or 1461501637330902918203684832716283019655932542976. 任何人都可以通過匿名連接(例如TOR網絡或VPN網絡)訪問比特幣網絡,並提交或接收交易,這些交易只顯示了他的公鑰。但是,如果某人反復使用相同的公鑰,則可以將所有交易關聯到同一所有者。比特幣網絡允許您生成任意數量的錢包,每個錢包都有自己的私鑰和公鑰。這樣一來,您就可以在不同的錢包中接收付款,並且除非您將所有接收到的比特幣發送到單個錢包中,否則任何人都無法知道您擁有所有這些錢包的私鑰。可能的比特幣地址總數為2???或1461501637330902918203684832716283019655932542976。 This large number protects the network from possible attacks while allowing anyone to owna wallet. 在允許任何人擁有錢包的同時,這一龐大的數目可保護網絡免受可能的攻擊。 With this setup, there is still a major security hole that could be exploited to recall bitcoins after spending them. Transactions are passed from node to node within the network, so the order in which two transactions reach each node can be different. An attacker could send a transaction, wait for the counterpart to ship a product, and then send a reverse transaction back to his own account. In this case, some nodes could receive the second transaction before the first and therefore consider the initial payment transaction invalid, as the transaction inputs would be marked as already spent. How do you know which transaction has been requested first? It’s not secure to order the transactions bytimestampbecauseit could easily be counterfeit. Therefore, there is no way to tell if atransaction happened before another, and this opens up the potential for fraud. 通過這種設置,仍然存在一個主要的安全漏洞,在花費比特幣後,可以利用該漏洞來召回比特幣。事務在網絡中從一個節點傳遞到另一個節點,因此兩個事務到達每個節點的順序可以不同。攻擊者可以發送交易,等待對方發送產品,然後將反向交易發送回自己的帳戶。在這種情況下,某些節點可以在第一筆交易之前收到第二筆交易,因此,由於交易輸入將被標記為已花費,因此認為初始支付交易無效。您怎麼知道先請求哪個交易?按時間戳訂購交易是不安全的,因為它很容易被偽造。因此,無法判斷交易是否先於另一筆交易進行,這會增加欺詐的可能性。 If this happens, there will be disagreement among the network nodes regarding the order of transactions each of them received. The blockchain system has been designed to use node agreement to order transactions and prevent the fraud described above. 如果發生這種情況,網絡節點之間在每個節點接收到的交易順序上將存在分歧。因此,區塊鏈系統已設計為使用節點協議來訂購交易並防止上述欺詐行為。 The bitcoin network orders transactions by grouping them intoblocks; each block contains a definite number of transactions and a link to the previous block. This is what puts one block after the other in time. Blocks are therefore organized into a time-related chain (Fig. 6) that gives the name to the whole system:blockchain. 比特幣網絡通過將交易分組來對交易進行排序;每個區塊都包含一定數量的交易以及到上一個區塊的鏈接。這就是將一個塊放在另一個塊之後的原因。因此,將塊組織成一個與時間相關的鏈(圖6),該鏈為整個系統命名:區塊鏈。
Fig. 6 —The block chain sequence structure simplified 圖6 —簡化的區塊鏈序列結構 Transactions in the same block are considered to have happened at the same time, and transactions not yet in a block are considered unconfirmed. Each node can group transactions into a block and broadcast it to the network as a suggestion for which block should be next. Since any node can suggest a new block, how does the system agree on which block should be the next? 同一區塊中的事務被視為同時發生,而尚未在區塊中的事務被視為未確認。每個節點都可以將事務分組為一個塊,然後將其廣播到網絡,作為對下一個塊的建議。由於任何節點都可以建議一個新的塊,系統如何同意下一個塊? To be added to the blockchain, each blockmust contain the answer to a complex mathematical problem created using an irreversiblecryptographic hash function. The only way to solve such a mathematical problem is to guess random numbers that,combined with the previous block content, generate a defined result. It could take about a year for a typical computer to guess the right number and solve the mathematical problem. However, due to the large number of computers in the network that are guessing numbers, a block is solved on average every 10minutes. The node that solves the mathematical problem acquires the right toplace the next block on the chain and broadcast it to the network. 要添加到區塊鏈中,每個區塊必須包含使用不可逆的密碼哈希函數創建的複雜數學問題的答案。解決此類數學問題的唯一方法是猜測隨機數,該隨機數與先前的塊內容結合可生成定義的結果。典型的計算機可能需要大約一年的時間才能猜出正確的數字並解決數學問題。但是,由於網絡中有大量正在猜測數字的計算機,因此平均每10分鐘就會解決一個塊。解決數學問題的節點獲得將下一個塊放置在鏈上並將其廣播到網絡的權利。 And what if two nodes solve the problem at the same time and send their blocks to the network simultaneously? In this case, both blocks are broadcast and each node builds on the block that it received first. However, the blockchain system requires each node to build immediately on the longest blockchain available. So if there is ambiguity about which is the last block, as soon as the next block is solved, each node will adopt the longest chain as the only option. 如果兩個節點同時解決問題並將它們的塊同時發送到網絡,該怎麼辦?在這種情況下,兩個塊都被廣播,並且每個節點都在它首先接收的塊上構建。但是,區塊鏈系統要求每個節點立即在可用的最長區塊鏈上構建。因此,如果不清楚哪個塊是最後一個塊,則在解決下一個塊時,每個節點將採用最長的鏈作為唯一選擇。
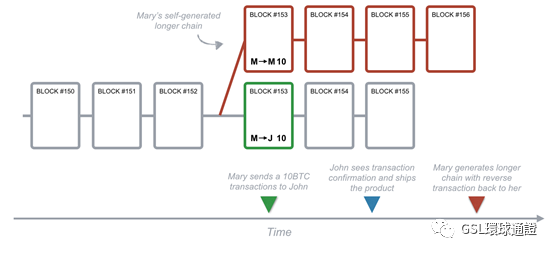
Fig.7 - Endof chain ambiguity logic 圖7-結束鏈歧義邏輯 Due to the low probability of solving blocks simultaneously, it’s almost impossible that multiple blocks would be solved at the same time over and over, building different “tails,” so the whole blockchain stabilizes quickly to one single string of blocks that every node agrees on. 由於同時解決區塊的可能性低,幾乎不可能一次又一次地解決多個區塊,建立不同的“尾巴”,因此整個區塊鏈可以快速穩定到每個節點都同意的單個字符串區塊。 A disagreement about which block represents the end of the chain tail opens up the potential for fraud again. If a transaction happens to be in a block that belongs to a shorter tail (like block B in Fig. 7), once the next block is solved, this transaction, along with all others in its block, will go back to the unconfirmed transactions. 關於哪個塊代錶鏈尾的末端的分歧,再次打開了欺詐的可能性。如果某個交易恰好位於屬?較短尾部的區塊中(如圖7中的區塊B),則在解決了下一個區塊後,該交易以及該區塊中的所有其他交易將返回到未確認的交易中。 Transactions in the Bitcoin blockchain system are protected by a mathematical race: Any attacker is competing against the whole network. 比特幣區塊鏈系統中的交易受到數學競賽的保護:任何攻擊者都在與整個網絡競爭。 Let’s see how Mary could leverage this end-of-chain ambiguity to perform a double-spending attack. Mary sends money to John, John ships the product toMary. Since nodes always adopt the longer tail as the confirmed transactions,if Mary could generate a longer tail that contains a reverse transaction with the same input references, John would be out of both his money and his product. 讓我們來看看Mary如何利用這種鏈末模糊性來進行一次雙重支出攻擊。瑪麗寄錢給約翰,約翰將產品寄給瑪麗。由於節點始終採用較長的尾巴作為已確認的交易,因此,如果Mary可以生成包含相同反向引用的反向交易的較長的尾巴,則John將會失去金錢和產品。
Fig. 8 -Mary’s double-spending attack 圖8-瑪麗的雙花攻擊 How does the system prevent this kind of fraud? Each block contains a reference to the previous block(see Fig. 6). That reference is part of the mathematical problem that needs to be solved in order to spread the following block to the network. So, it’s extremely hard to pre-compute a series of blocks due to the high number of random guesses needed to solve a block and place it on the blockchain. Mary is in a race against the rest of the network to solve the math problem that allows her to place the next block on the chain. Even if she solves it before anyone else, it’s very unlikely she could solve two, three, or more blocks in a row, since each time she is competing against the whole network. 系統如何防止此類欺詐?每個塊都包含對前一個塊的引用(請參見圖6)。該參考是數學問題的一部分,需要將其擴展到網絡上才能解決。因此,由於要求解一個區塊並將其放置在區塊鏈上,需要大量隨機猜測,因此很難預先計算一系列區塊。瑪麗正在與其他網絡競爭,以解決數學問題,使她能夠將下一個區塊放在鏈上。即使她先於其他人解決了問題,也不太可能連續解決兩個,三個或更多的問題,因為每次她都在與整個網絡競爭。 Could Mary use a super-fast computer to generate enough random guesses to compete with the whole network in solving blocks? Yes, but even with a very, very fast computer,due to the large number of members in the network, it’s highly unlikely Mary could solve several blocks in a row at the exact time needed to perform a double-spending attack. 瑪麗可以使用超快速計算機生成足夠的隨機猜測值來與整個網絡競爭以解決區塊嗎?是的,但是即使網絡非常快,由於網絡中的成員數量眾多,瑪麗極不可能在執行雙重花費攻擊的確切時間連續解決幾個區塊。 She would need control of 50 percent of the computing power of the whole network to havea 50 percent chance of solving a block before some other node does — and even in this case, she’d only have a 25 percent chance of solving two blocks in a row. The more blocks to be solves in a row, the lower the probability of her success. Transactions in the bitcoin blockchain system are protected by a mathematical race: Any attacker is competing against the entire network. 她將需要控制整個網絡50%的計算能力,才能有50%的機會在其他節點之前解決一個塊-即使在這種情況下,她也只有25%的機會解決兩個塊連續。連續解決的障礙越多,成功的可能性就越低。比特幣區塊鏈系統中的交易受到數學競賽的保護:任何攻擊者都在與整個網絡競爭。 Therefore,transactions grow more secure with time. Those included in a block confirmed one hour ago, for example, are more secure than those in a block confirmed in the last 10 minutes.Since a block is added to the chain every 10 minutes on average, a transaction included in a block for the first time an hour ago has most likely been processed and is now irreversible. 因此,隨著時間的推移,交易變得越來越安全。例如,在一小時前確認的區塊中包含的安全性比最近10分鐘內確認的區塊中的安全性更高。由於平均平均每10分鐘將一個區塊添加到鏈中,因此一個小時前第一次包含在該區塊中的交易很可能已被處理,現在是不可逆的。
Fig. 9 -Blockchain transactions security 圖9-區塊鏈交易安全 Mining Bitcoin 挖礦比特幣 In order to send bitcoins, you need to reference an incoming transaction to your own wallet. This applies to every single transaction across the network. So, where do bitcoins come from in the first place? 為了發送比特幣,您需要將傳入交易引用到您自己的錢包中。這適用於網絡上的每筆交易。那麼,比特幣從何而來呢? As a way to balance the deflationary nature of bitcoin due to software errors and wallet password loss, a reward is given to those who solve the mathematical problem of each block. The activity of running the bitcoin blockchain software in order to obtain these bitcoin rewards is called “mining” — and it’s very much like mining gold. 作為平衡由於軟件錯誤和錢包密碼丟失而導致的比特幣通縮性質的一種方式,給予解決每個區塊數學問題的人以獎勵。為了獲得這些比特幣獎勵而運行比特幣區塊鏈軟件的活動稱為“採礦”,這非常類似于開採黃金。 Rewards are the main incentive for private people to operate the nodes, thus providing the necessary computing power to process transactions and stabilize the blockchain network. 獎勵是私人操作節點的主要動機,從而為處理交易和穩定區塊鏈網絡提供了必要的計算能力。 Because it takes a long time for a typical computer to solve a block(about one year on average), nodes band together in groups that divide up the number of guesses to solve the next block. Working as a group speeds up the process of guessing the right number and getting the reward, which is then shared among group members.These groups are calledmining pools. 因為一台典型的計算機要花很長時間才能解決一個塊(平均大約一年),所以節點按組分組在一起,將猜測的數目相除以解決下一個塊。分組工作可以加快猜測正確數字並獲得獎勵的過程,然後由小組成員共享。這些組稱為採礦池。 Some of these mining pools are very large and represent more than 20 percent of the total network computing power. This has clear implications for network security, as seen in the double-spend attack example above. Even if one ofthese pools could potentially gain 50 percent of the network computing power,the further back along the chain a block goes, the more secure the transactions within it become. 其中一些採礦池非常大,占網絡總計算能力的20%以上。如上面的雙花攻擊示例所示,這對網絡安全具有明顯的影響。即使這些池中的一個可能潛在地獲得了50%的網絡計算能力,一個區塊沿著鏈條走得越遠,其中的交易就越安全。 However,some of these mining pools with substantial computing power have decided to limit their members in order to safeguard overall network security. 但是,其中一些具有強大計算能力的採礦池已決定限制其成員,以維護整體網絡安全。 Since the overall network computing power is likely to increase over time due to technological innovation and the increasing number of nodes, the blockchain system recalibrates the mathematical difficulty of solving the next block to target 10 minutes on average for the entire network. This ensures the network’s stability and overall security. 由於技術創新和節點數量的增加,總體網絡計算能力可能會隨著時間的推移而增加,因此,區塊鏈系統重新校準了求解下一個區塊的數學難度,以使整個網絡的平均目標時間為10分鐘。這樣可以確保網絡的穩定性和整體安全性。 Moreover,every four years the block reward is cut in half, so mining bitcoin (running the network) gets less interesting over time. To encourage nodes to keep operating, small reward fees can be attached to each transaction; these rewards are collected by the node that successfully includes such transactions in ablock and solves its mathematical problem. Due to this mechanism, transaction sassociated with a higher reward are usually processed faster than those associated with a low reward. What this means is that, when sending atransaction, you can decide if you’d like to process it faster (more expensive)or cheaper (takes more time). Transaction fees in the bitcoin network are currently very small compared with what banks charge, and they’re not associated with the transaction amount. 此外,每四年塊獎勵減少一半,因此隨著時間的推移,開採比特幣(運行網絡)的興趣就減少了。為了鼓勵節點繼續運行,可以向每筆交易收取少量獎勵費用;這些獎勵是由成功收集此類交易的節點收集的,並解決了其數學問題。由於這種機制,與高報酬相關聯的交易通常比與低報酬相關聯的交易處理得更快。這意味著,在發送交易時,您可以決定是想更快地處理(更昂貴)還是更便宜地處理(花費更多時間)。與銀行收取的費用相比,目前比特幣網絡中的交易費用很小,並且與交易金額無關。 Blockchain Benefits and Challenges 區塊鏈的好處和挑戰 Now that you have a general understanding of how the blockchain works, let’s take aquick look at why it’s so interesting. Using blockchain technology has remarkable benefits: You have complete control of the value you own; there is no third party that holds your value or can limit your access to it. The cost to perform a value transaction from and to anywhere on the planet is very low.This allowsmicropayments. Value can be transferred in a few minutes, and the transaction can be considered secure after a few hours, rather than days or weeks. Anyone at any time can verify every transaction made on the blockchain, resulting in full transparency. 現在,您已經對區塊鏈的工作原理有了大致的瞭解,下面讓我們快速看一下為什麼它如此有趣。 使用區塊鏈技術具有顯著的優勢: 您可以完全控制自己擁有的價值;沒有第三方擁有您的價值或可以限制您的使用。 從地球上任何地方進行價值交易的成本非常低。這允許小額付款。 可以在幾分鐘內轉移價值,並且可以在幾小時而不是幾天或幾周後認為交易是安全的。 任何人都可以隨時驗證在區塊鏈上進行的每筆交易,從而實現完全透明。 It’s possible to leverage the blockchain technology to builddecentralized applicationsthat would be able to manage information and transfer value fast and securely. 可以利用區塊鏈技術構建去中心化的應用程序,這些應用程序可以快速安全地管理信息並轉移價值。 However,there are a few challenges that need to be addressed: Transactions can be sent and received anonymously. This preserves user privacy, but it also allows illegal activity on the network. 但是,有一些挑戰需要解決:交易可以匿名發送和接收。這樣既可以保護用戶的隱私,又可以允許網絡上的非法活動。 Though many exchange platforms are emerging, and digital currencies are gaining popularity,it’s still not easy to trade bitcoins for goods and services. 儘管出現了許多交易平臺,並且數字貨幣越來越流行,但是用比特幣交易商品和服務仍然不容易。 Bitcoin,like many other cryptocurrencies, is very volatile: There aren’t many bitcoins available in the market and the demand is changing rapidly. Bitcoin price is erratic, changing based on large events or announcements in the cryptocurrencies industry. 像許多其他加密貨幣一樣,比特幣也非常不穩定:市場上沒有多少比特幣可用,需求也在迅速變化。比特幣價格不穩定,會根據加密貨幣行業的重大事件或公告而變化。 Overall,the blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize several industries, from advertising to energy distribution. Its main power lies in its decentralized nature and ability to eliminate the need for trust. 總體而言,區塊鏈技術具有革新廣告,能源分配等多個行業的潛力。它的主要力量在於其分散的性質和消除信任需求的能力。 New use cases are arising all the time — like the possibility of creating a fully decentralized platform that runs smart contracts like Ethereum. But it’s important to remember that the technology is still in its infancy. New tools are being developed every day to improve blockchain security while offering abroader range of features, tools, and services. 新的用例無時無刻不在出現-諸如創建一個完全分散的平臺的可能性,該平臺運行像以太坊這樣的智能合約。但是請務必記住,該技術仍處於起步階段。每天都在開發新工具,以改善區塊鏈安全性,同時提供更廣泛的功能,工具和服務。 本文来源:链上兵哥 —- 编译者/作者:链上兵哥 玩币族申明:玩币族作为开放的资讯翻译/分享平台,所提供的所有资讯仅代表作者个人观点,与玩币族平台立场无关,且不构成任何投资理财建议。文章版权归原作者所有。 |
How Does the Blockchain Work? 區塊鏈如何運作?
2020-04-01 链上兵哥 来源:火星财经
LOADING...
相关阅读:
- 区块链巨头火币集团计划向DeFi投资数百万美元2020-08-05
- 以色列将启动区块链平台2020-08-05
- 以太坊和Reddit:5天挑战2020-08-05
- 唯链与ADIL联手开发新的食品供应链解决方案2020-08-04
- 区块链神算子:8.4晚间行情弱势震荡 后续操作切勿追涨杀跌2020-08-04